Your cart is currently empty!
American Built, Affordable Price. Check out the all new TrueView1 LITE
LiDAR
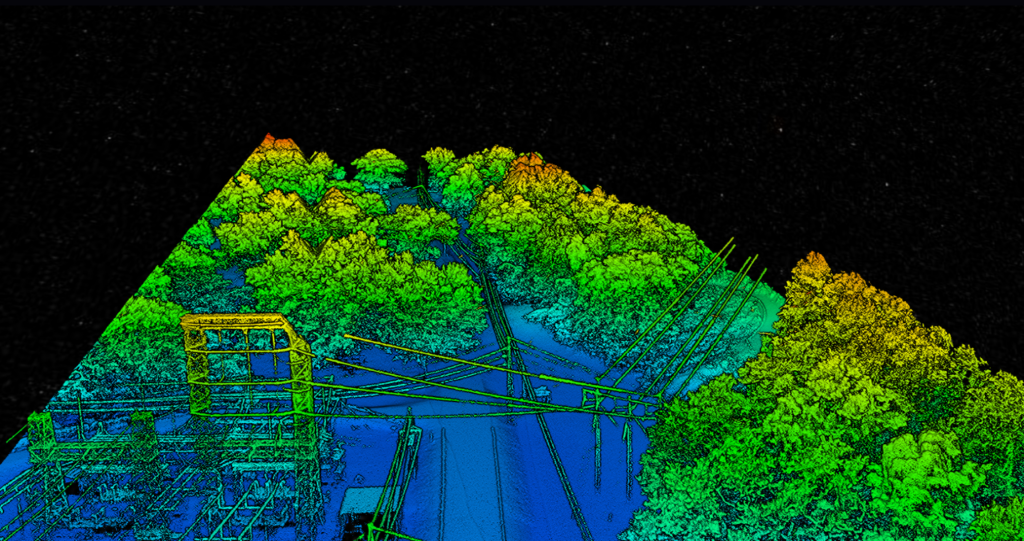
Unlock Unparalleled Precision with Drone-Based LiDAR.
Harness the power of Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) to capture highly accurate 3D data for a wide range of enterprise applications. Once exclusive to manned aircraft, advancements in drone technology, including sophisticated cameras, Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), and extended battery life, now allow for the integration of these precise sensors onto unmanned aerial vehicles. Experience a new level of detail and insight with our cutting-edge LiDAR drone solutions.
Related Products
-
 DJI Matrice 300 RTK$12,179.00
DJI Matrice 300 RTK$12,179.00
